
APM Integrity, part of GE Digital's Asset Performance Management, equips organizations to enable a closed loop mechanical integrity program across the enterprise. This comprehensive inspection solution helps operators to reduce risk, lower inspection costs, and ensure regulatory compliance relative to their fixed assets. Leveraging an integrated set of tools, APM Integrity enables users to calculate risk and the remaining useful life of assets to generate, implement, and execute optimized inspection strategies while streamlining auditability and compliance governance. The solution also facilitates compliance with various Process Safety Management (PSM) requirements such as process hazard analysis, mechanical integrity, and management of change.
Setting the Foundation of a Sustainable Mechanical Integrity Program with Risk-Based Inspection
Setting the Foundation of a Sustainable Mechanical Integrity Program with Risk-Based Inspection
Fully integrate compliance and integrity initiatives across an enterprise with corporate asset hierarchy and EAM system integration–resulting in higher asset availability and lower catastrophic incident probability.
Develop and optimize inspection strategies through risk based inspection (RBI) methodologies (API RP 580, 581) and enable compliance with OSHA 1910.119 process safety management requirements and ISA/IEC safety standards.
Automatically re-analyze integrity and safety risk, based on real-time data field information and intelligent actions executed on pre-defined conditions.
1-6 %
Increased availability3-40 %
EH&S incident reduction5-25 %
Gain in employment productivity
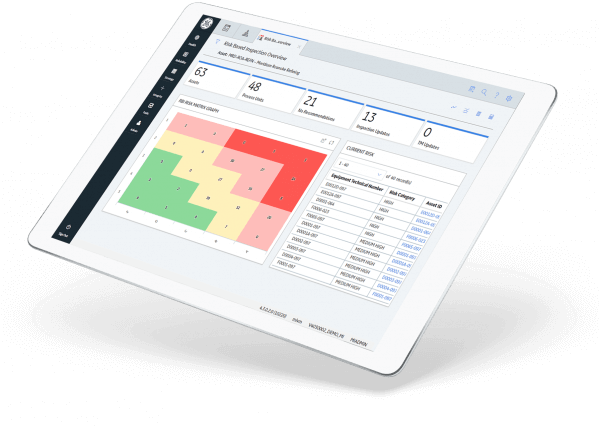
Most inspection programs are mandated by regulatory agencies with the power to apply significant penalties for non-compliance. To improve cost-effectiveness, many organizations are turning to RBI as a preferred methodology. This RBI methodology is based on and has been certified as complying with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards 580 and 581. This aptitude supports the ability to assess the probability and consequences of failures to optimize inspection precision based on the overall risk. The visual surveillance and inspection of both fixed and linear assets is a critical element in assessing the current condition of the asset and avoiding equipment failures. RBI can be seamlessly integrated into inspection management and maintenance programs.
Inspection management provides the ability to establish large-scale inspection programs designed to comply with federal, state, and local requirements—including API standards. This inclination allows asset owners and operators to manage inspection plans on several asset classes, document the condition of the asset, and track inspection recommendations to closure. Also part of this capability is the ability to capture inspection data in the field using a mobile device. This enables users to employ the functionality of inspection data collection to complete required inspection checklists, capture images, and make recommendations in an on or off-line mode. The data collected while the device is offline is saved securely on the device until it is reconnected and synchronized with APM.
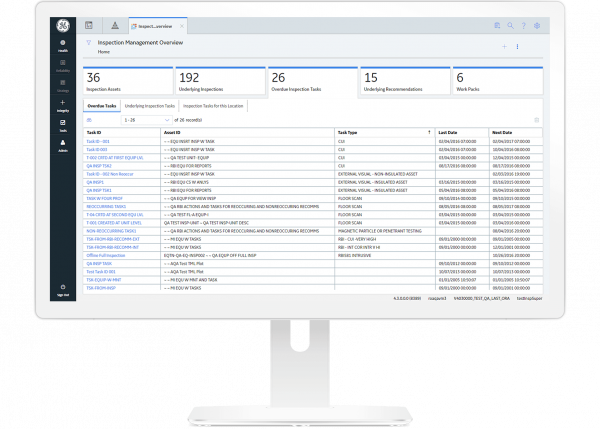
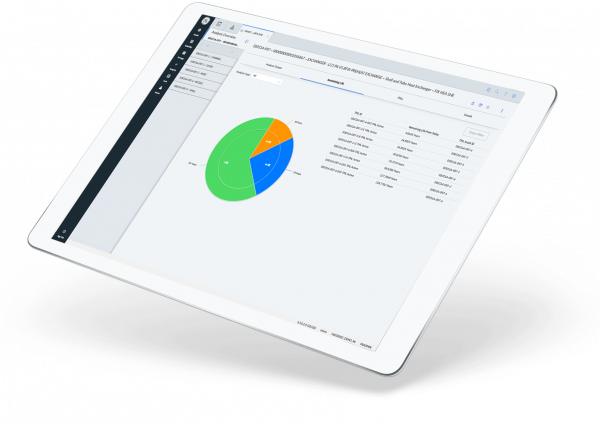
Effective density measurement activities are an essential component of a mechanical integrity program. This capability provides the opportunity to manage large-scale corrosion and thickness measurement programs for stationary equipment, such as pipelines, piping, vessels, exchangers, tanks, boilers, etc. Key elements of the density monitoring feature include the ability to: calculate the minimum thickness required to operate the equipment safely, manage thickness measurement data, analyze corrosion rate, as well as, provide next-inspection data and retirement-data inspections. These calculated values can be seamlessly integrated back into the EAM/CMMS systems and other features within APM.
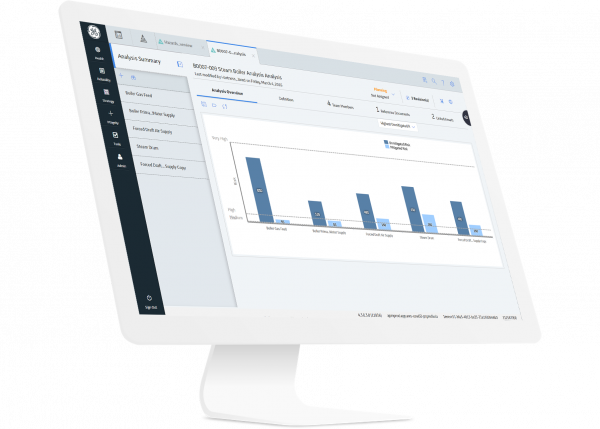
Based on international standards, such as the IEC 61882 Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP Studies) - Application Guide, the risk analysis capability is both a regulatory requirement as well as an integral part of an overall risk management process—focused on identifying and assessing risks and managing the reduction of those risks. Additionally, hazard or risk analysis is integrated within capabilities in the APM Strategy solution.
The MOC capability follows a systematic approach to delivering a change, taking into consideration aspects of operations that will or could be influenced by the change. By using MOC, changes are tackled as “change projects''. In a change project, modifications are formally introduced, approved, and implemented as assignments.
MOC provides a flexible solution for creating and managing change projects, communicating changes to team members, and enforcing an approval system to provide accountability for the change. When a change is being implemented, it directly or indirectly has an impact on other families within APM. In MOC, users can associate a change project with records from other families in APM that are possibly influenced by the change. Such records are called "changed elements." For example, when the change involves replacing the existing pressure relief devices that were identified as independent protection layers, with a different manufacturer's device, the LOPA assessment with which the equipment is associated may be impacted. In this case, the affected LOPA record is a changed element and you can associate the LOPA record with the change project. In turn, it provides organizations with a greater degree of audibility, which is essential in industries that require MOC as a PSM regulatory compliance requirement.